First 10 Fibonacci numbers:
0
1
1
2
3
5
8
13
21
34
Hello, Nitin! Welcome to our program.
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date"]
# Display the list
print("Original list:", fruits)
# Add an item to the list
fruits.append("elderberry")
print("After adding an item:", fruits)
# Remove an item from the list
fruits.remove("cherry")
print("After removing an item:", fruits)
# Reverse the list
fruits.reverse()
print("Reversed list:", fruits)
# Sort the list
fruits.sort()
print("Sorted list:", fruits)
# Find the index of an item
index = fruits.index("date")
print("Index of 'date':", index)
# Insert an item at a specific position
fruits.insert(2, "fig")
print("After inserting an item:", fruits)
# Count occurrences of an item
count = fruits.count("apple")
print("Count of 'apple':", count)
# Clear the list
fruits.clear()
print("After clearing the list:", fruits)
Original list: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date']
After adding an item: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date', 'elderberry']
After removing an item: ['apple', 'banana', 'date', 'elderberry']
Reversed list: ['elderberry', 'date', 'banana', 'apple']
Sorted list: ['apple', 'banana', 'date', 'elderberry']
Index of 'date': 2
After inserting an item: ['apple', 'banana', 'fig', 'date', 'elderberry']
Count of 'apple': 1
After clearing the list: []
# Create a dictionary
person = {
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"city": "New York"
}
# Accessing elements
print(person["name"]) # Output: John
print(person.get("age")) # Output: 30
# Adding elements
person["job"] = "Engineer"
print(person) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York', 'job': 'Engineer'}
# Removing elements
del person["age"]
print(person) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'city': 'New York', 'job': 'Engineer'}
# Iterating through a dictionary
for key, value in person.items():
print(f"{key}: {value}")
# Checking if a key exists
if "city" in person:
print(f"City is: {person['city']}") # Output: City is: New York
# Dictionary length
print(len(person)) # Output: 3
# Nested dictionaries
person['address'] = {
'street': '123 Main St',
'zipcode': '10001'
}
print(person['address']['street']) # Output: 123 Main St
John
30
{'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York', 'job': 'Engineer'}
{'name': 'John', 'city': 'New York', 'job': 'Engineer'}
name: John
city: New York
job: Engineer
City is: New York
3
123 Main St
Choose an operation:
1. Calculate Square Root
2. Calculate Mean of a List of Numbers
Square root of 25.0 is 5.0
Weather in London:
Temperature: 18.60°C
Humidity: 84%
Description: Broken clouds
"""
Program: List Calculation
Description:
This Python program takes a list of numbers, iterates through it, and performs two calculations:
1. It calculates the sum of all even numbers in the list.
2. It calculates the product of all odd numbers in the list.
Usage:
1. Define a list of numbers in the 'numbers' variable.
2. The program will iterate through the list and perform the calculations.
3. The results (sum of even numbers and product of odd numbers) will be displayed.
Example:
If the 'numbers' list contains [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], the program will output:
Sum of even numbers: 30
Product of odd numbers: 945
"""
# Define a list of numbers
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
# Initialize variables for sum of even numbers and product of odd numbers
even_sum = 0
odd_product = 1
# Iterate through the list and perform calculations
for number in numbers:
if number % 2 == 0: # Check if the number is even
even_sum += number
else:
odd_product *= number
# Print the results
print("Sum of even numbers:", even_sum)
print("Product of odd numbers:", odd_product)
Sum of even numbers: 30
Product of odd numbers: 945
# Import the statistics module which provides functions to perform statistical operations.
import statistics as stats
# Initialize a list of numbers. This will serve as the sample data
# for which we want to compute the mean, median, and standard deviation.
numbers = [2, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 9]
# Define a function to calculate the mean of a list of numbers.
def calculate_mean(nums):
"""
Calculate the mean (average) of a given list of numbers.
:param nums: A list containing numeric values.
:return: The arithmetic mean of the numbers.
"""
# To compute the mean, sum all elements in the list
# and divide by the number of elements.
return sum(nums) / len(nums)
# Define a function to determine the median of a list of numbers.
def calculate_median(nums):
"""
Calculate the median (middle value) of a given list of numbers.
:param nums: A list containing numeric values.
:return: The median value.
"""
# First, sort the list in ascending order to determine the middle values.
sorted_nums = sorted(nums)
# Find the number of elements in the sorted list.
n = len(sorted_nums)
# Determine if the number of elements is odd.
if n % 2 == 1:
# If odd, the median is the single middle number in the sorted list.
return sorted_nums[n//2]
else:
# If even, the median is the average of the two middle numbers in the sorted list.
left = sorted_nums[(n-1)//2]
right = sorted_nums[n//2]
return (left + right) / 2
# Define a function to calculate the standard deviation of a list of numbers.
def calculate_std_dev(nums):
"""
Calculate the standard deviation (a measure of variability)
of a given list of numbers.
:param nums: A list containing numeric values.
:return: The standard deviation of the numbers.
"""
# The stdev function from the statistics library is used
# to easily compute the standard deviation.
return stats.stdev(nums)
# Now, we'll utilize our defined functions to compute and display
# the mean, median, and standard deviation of our sample data.
# Display the computed mean of the sample data.
print(f"Mean: {calculate_mean(numbers)}")
# Display the computed median of the sample data.
print(f"Median: {calculate_median(numbers)}")
# Display the computed standard deviation of the sample data.
print(f"Standard Deviation: {calculate_std_dev(numbers)}")
Mean: 5.0
Median: 4.5
Standard Deviation: 2.138089935299395
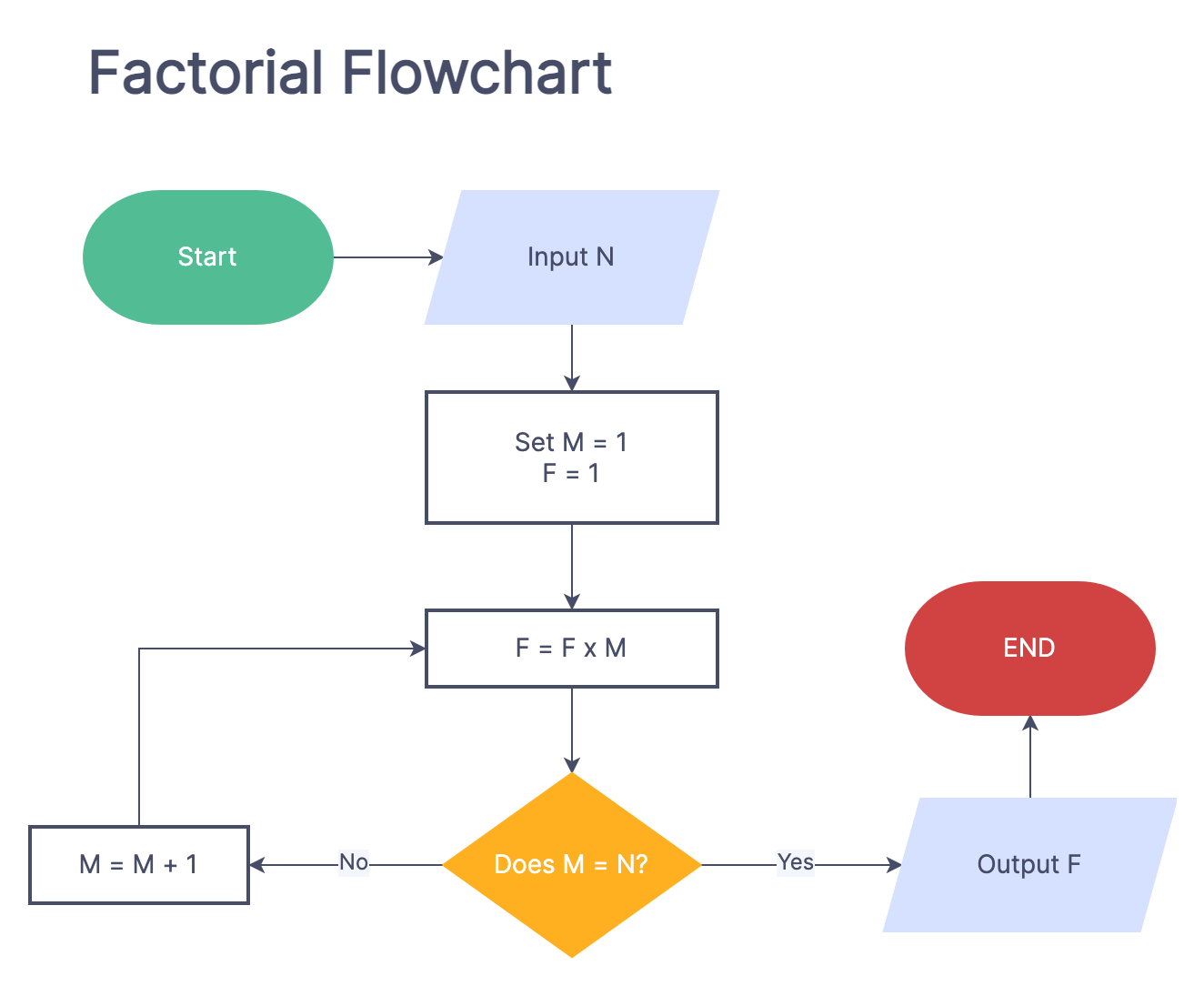
def factorial(n):
"""
Calculates the factorial of a given number.
:param n: Number for which factorial needs to be calculated.
:return: Factorial of the given number.
"""
if n < 0:
raise ValueError("Factorial is not defined for negative numbers.")
result = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
result *= i
return result
def get_input_and_calculate_factorial():
"""
Gets input from the user and prints the factorial.
Incorporates error-handling to ensure valid input and outputs.
"""
try:
# Get input from the user.
num = int(input("Enter a number to calculate its factorial: "))
# Check if the number is negative, zero, or positive.
if num < 0:
print("Sorry, factorial does not exist for negative numbers")
elif num == 0:
print("The factorial of 0 is 1")
else:
print(f"The factorial of {num} is {factorial(num)}")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}. Please enter a valid number.")
def tester():
"""
Tester function to validate the functionality of the factorial function.
"""
test_cases = [-1, 0, 5, 7]
expected_results = [None, 1, 120, 5040]
for num, expected in zip(test_cases, expected_results):
try:
result = factorial(num)
assert result == expected, f"Expected {expected}, but got {result} for input {num}"
print(f"Test case for {num} passed!")
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Test case for {num} raised error as expected: {e}")
except AssertionError as e:
print(f"Test case for {num} failed: {e}")
# Uncomment the line below if you want to manually input numbers and check results.
# get_input_and_calculate_factorial()
# Run the tester function to validate functionality.
tester()
Test case for -1 raised error as expected: Factorial is not defined for negative numbers.
Test case for 0 passed!
Test case for 5 passed!
Test case for 7 passed!